Computer Software
By Notes Vandar
2.1 Introduction to Software
Software is a set of computer programs that instruct computer what to do, enabling it to perform specific tasks. Unlike hardware, which is the physical part of a computer, software is intangible and cannot be touched. It acts as the interface between the user and the hardware, enabling communication and execution of different operations. Essentially, software acts as the brain of the computer, controlling its operations and allowing users to interact with it.
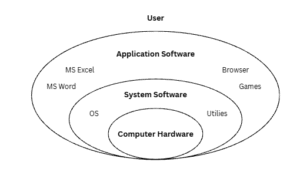
Fig: Computer Software
2.2 Types of Software
There are two types of software:
System Software
System software is a collection of programs that manage the internal operations of a computer, such as controlling input/output devices and handling storage. It is usually supplied by the manufacturer and makes the use of a computer more efficient and easier. System software directly operates the hardware and provides basic functionality for users and application software to run smoothly. It also controls devices like monitors, printers, and storage units, while acting as an interface between hardware and user applications. Since hardware understands only machine language (0s and 1s) and applications work in human-readable languages, system software enables their communication. Its main purposes are to provide basic functions, control hardware, and serve as a link between the user, application software, and hardware. Examples includes windows, macOS, Linux, IOS, android
Application Software
Application software is the software written by users to solve specific problems or perform user-oriented tasks with the help of a computer. It may consist of a single program or a set of programs designed for particular applications. This type of software provides functions beyond the basic operations of the computer and is created to fulfill the needs of end-users. Examples include word processors, spreadsheets, database management systems, inventory control, payroll programs, CAD/CAM applications, MS Access, Oracle, and MS Word.
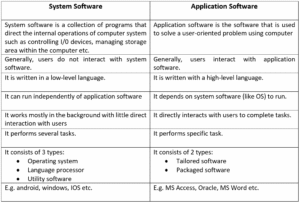
Fig: System vs Application software
2.3 Program vs Software
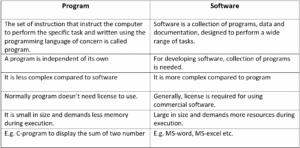
Fig: Program vs Software
Word Processor (MS Word)
Word processing software is used to create, edit, format, and print text documents. MS Word is a popular word processor created by Microsoft Corporation used for writing letters, reports, assignments, and other text-based documents.
Functions of MS Word:
- Allows typing and composing text
- Allows editing font styles, colors, alignment, and paragraph styles.
- Detects and corrects spelling and grammatical errors.
- Add images, tables, charts, hyperlinks, and shapes.
- Provides options to print documents or save as PDF.
Spreadsheet Software (MS Excel)
Spreadsheet software is used to store, organize, and analyze data in tabular form. MS Excel is also created by Microsoft Corporation widely used for calculations, creating charts, and managing numerical data.
Functions of MS Excel:
- Enter and store data in rows and columns.
- Perform calculations using built-in formulas.
- Sort, filter, and analyze large sets of data.
- Represent data visually using bar, line, pie charts, etc.
- Print worksheets or save in different formats.
2.4 Computer Virus and Antivirus
A computer virus is a type of malicious software (malware) that is designed to disrupt the normal functioning of a computer. It has the ability to replicate itself and attach to other files or programs, which allows it to spread when those files are shared, copied, or executed on another system. Viruses can cause various harmful effects such as slowing down the system, corrupting or deleting files, stealing data, or even crashing the entire computer. They often spread through infected email attachments, downloads, removable devices, or insecure networks.
Types of computer virus
Boot Sector Virus: Infects the master boot record of storage devices, preventing the system from booting properly.
File Infector Virus: Attaches itself to executable files (.exe, .com) and spreads when these files are run.
Macro Virus: Targets macro scripts in applications like Microsoft Word or Excel, spreading through infected documents.
Resident Virus: Lodges itself in the system’s memory and can infect files and programs during execution.
Polymorphic Virus: Changes its code or appearance to avoid detection by antivirus software.
Multipartite Virus: Spreads through multiple methods, such as infecting both the boot sector and executable files.
Direct Action Virus: Activates when a specific action is performed, like opening a file, and then executes its payload.
Browser Hijacker: Alters browser settings to redirect users to malicious websites.
Sources of Computer Virus
Some of the common sources of computer viruses are:
- Email attachments
- Removable storages devices like USB
- Downloading from untrusted websites
- File sharing networks
- Infected software installers
- Pop-up ads and malicious links
Symptoms of computer virus
Some of the symptoms of computer viruses are:
- File being renamed, deleted, or duplicated unexpectedly.
- Programs taking a long time to load or not responding.
- Unusual increase in disk space usage or file sizes.
- Strange pop-ups or messages appearing on the screen.
- Unexpected network activity or automatic sending of emails.
- Frequent error messages or system crashes.
Protection against computer virus
Some of the protection measures against computer viruses are:
- Installing latest antivirus software.
- Regularly update your operating system and applications to patch vulnerabilities.
- Avoid clicking suspicious links and downloading attachments.
- Keep backup copies of important data to recover in case of infection.
- Always scan USB drivers, external hard disks, and other removable media before user.
Anti-Virus
Antivirus software is an application software that is used to prevent, scan, detect and delete viruses from a computer. Antivirus products work by detecting, quarantining and/or deleting malicious code, to prevent malware from causing damage to your device. Originally developed to combat computer viruses, it now encompasses a broader range of protections against various threats like ransomware, spyware, and even zero-day attacks. It continuously scans files, programs, and the system for suspicious activity, protecting data and maintaining smooth system performance. Popular examples include Avast, Norton, Kaspersky, and Windows Defender.