Networking and Telecommunication
By Notes Vandar
Communication and its modes and components
Communication: The process of exchanging messages between sender and receiver through any medium using definite rules is called communication. If communication is done over a longer distance then it is called telecommunication.
Data communication: The process of exchanging data and information between several electronic means and media through any medium using a definite rule(protocol) is called data communication.
Components/Elements of communication
- Sender
- Receiver
- Medium
- Data
- Protocol: The set of rules through communication takes place.
Modes of communication:
- Simplex: Only the sender sends information, the receiver only receives the message. It is one-way communication. Eg, Television, radio
- Half duplex: Sender sends the data while the receiver receives the data and vice-versa. It is a two-way communication but one at a time Eg, Walkie-Talkie
- Full duplex: It is two-way communication in which the sender and receiver both can send and receive information at the same time. Eg, mobile communication.
Computer Network and its pros and cons
Computer network: A group of computers interconnected with each other through any medium using the definite protocol (rule) for the purpose of sharing data, information, hardware, software, and other resources. Services provided by the computer network.
- Data Sharing
- Print service
- File service
- Database service
- Application service
Advantages/merits/pros/benefits/importance of computer network.
- It allows several user computers to share data and information.
- Expensive hardware like printers, scanners, the fax can be shared in a network.
- Application programs and software can be shared in a network.
- We can easily communicate in real time i.e. faster communication.
- Easy to collect data through a centrally located server.
Disadvantages/de-merits/cons/limitations of computer network.
- Skilled manpower is required to install and operate a network.
- Expensive to install and operate.
- There may be security and privacy issues due to sharing.
- Viruses and malware may be shared in a network.
Transmission media and its types
Communication media/Transmission media/Communication channel
The medium through which data and information are transmitted from one point to another point in the form of signals is called transmission media. There are two types of transmission media.
A) Wired/bounded/guided media: The transmission media in which data are transmitted physically through cables or wire following a specified path.
a. Twisted pair: Wires are twisted with each other to reduce EMI(Electro Magnetic Interference).
- UTP(Unshielded Twisted Pair): Inner pair of twisted cables are not covered/unshielded with the outer jacket. Hence, it has more EMI.
- STP (Shielded Twisted Pair): Inner pair of twisted cables are covered/shielded with the outer jacket. Hence, it has less EMI.
b. Co-axial cable: This cable has higher bandwidth so, they are used in television broadcasting.
c. Fibre optics: These types of cable are made up of thin glass-like material where data are transmitted in the form of photons(light). They have high data transmission rate.
Media connector:
- Twisted pair use RJ-45
- Co-axial cable use BNC
- Fiber optics cable use ST-connector
B) Wireless/unbounded/unguided media: The transmission media in which data are not restricted to travel in a closed path rather they can travel in the open air. There is no physical connection between communicating devices hence, called wireless.
a. Microwave: The sender and receiver station must be in the same line of sight (LOS). They cannot penetrate obstacles. Used for longer-distance transmission. Satellites use microwave signals to uplink and downlink data from and to earth.
b. Radiowave: Sender and receiver station may not be in the same line of sight (LOS). They can penetrate obstacles. Used by FM stations and other local communicating stations.
c. Infrared: It uses an invisible red ray of light of the electromagnetic spectrum for communication purposes. Eg, television remotes, AC remotes, and many more.
Types of Computer Networks
Types of network
- LAN: It stands for Local Area Network which connects devices in smaller locations such as rooms, buildings, organizations, etc. It is suitable for a single organization. It generally uses guided media to connect devices.
- MAN: It stands for Metropolitan Area Network which can connect devices in larger geographical areas such as towns, cities, villages, etc. It consists of two or more two LANs. It uses wired as well as wireless media for connecting devices.
- WAN: It stands for Wide Area Network which is set in a larger geographical area across the city, nation, and even ocean. It is can be used by multiple organizations. Internet is an example of WAN, which is a public network all around the world. They use wireless media for communication.
Network architecture:
- Client-server: In this type of architecture the devices in a network are connected to the centrally located main computer of a network called the server. User computers are called clients. It provides more security and control in a network. The server allows to the mobilization of all the resources available in the network. Easier to collect data in centrally located servers.

Client Server Architecture
- Peer-to-peer: In this type, there is no presence of the main computer in a network, rather every computer in a network have the right to control and use resources. Every computer in this case is a client as well as a server. Hence there will be less safe.

Peer-to-Peer Architecture
Network Models:
- Centralized model: This is a client-server model in which every device of a network is connected to the centrally located main computer.
- Distributed model: This is the collection of several client-server models located at a different locations, all connected to a centrally located server.
Network topology and its types
Network topology: The physical layout, geographical orientation, connection pattern, or arrangement of computers or devices (nodes) in the network is called network topologies.Types:
1) Bus topology: In this topology, every device in the network is connected to a main single cable called a trunk or backbone. It is easy and cheaper to set up. It requires less amount of cables and adding new devices to a network is also easy. Whereas, if there is a fault in the main cable then the whole network will collapse. Fault finding is fairly difficult.

Bus Topology
2) Star topology: In this topology, every device in the network is connected to the centrally located device called the hub which allows us to easily expand the network. Fault finding is very easy in this type. The whole network depends upon the hub so, if it fails network will collapse. It is expensive to set up but is the most practical among all topologies.

Star Topology
3) Ring topology: In this topology, devices are connected with each other in a circular manner each device having equal rights and responsibilities. Failure in one device will collapse the whole network. Expanding the network is difficult and is not practical.

Ring Topology
4) Tree topology: It is the combination of bus and star topology. The whole network depends on the main cable and some parts depend on the hub so It is less reliable.
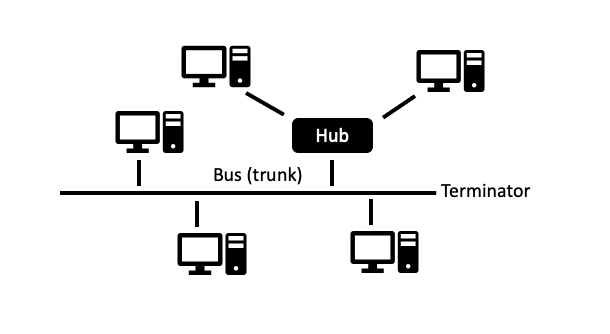
Tree Topology
5) Mesh topology: In this topology, networking devices are point-to-point connected with each other creating a mesh. If one device fails to work then it will not affect the whole network. It is expensive and difficult to set up.
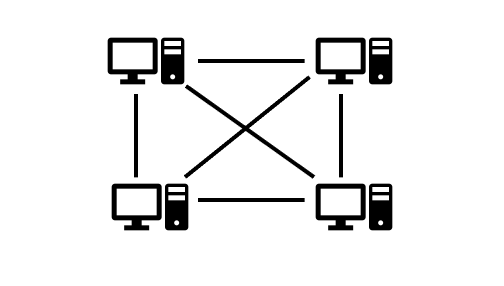
Mesh Topology
Some important terms to remember
a. Bandwidth: The amount of data that can travel in a given transmission medium in unit time is called its bandwidth. It is generally known as data transmission speed and measured in terms of bps (Bit per second)
b. Protocol: The set of rules that guides the communication in the network. It is the language used by computers and electronic devices to communicate with each other. For eg,
- TCP/IP: Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol
- HTTP: Hyper Text Transfer Protocol
- FTP: File Transfer Protocol
- SMTP: Simple Mail Transfer Protocol
- POP: Post Office Protocol
- ARP: Address Resolution Protocol
c. Network operating system (NOS): It is the collection of program that helps to mobilize and manages resources of the network. For eg, Windows NT, Linux, etc
Internetworking devices/hardware: Devices that are used to establish and expand networks are called internetworking devices.
- NIC(Network Interface card): It physically connects the computer system with a transmission cable.
- Router: Intelligent device that connects two or more networks. It facilitates finding the best route for data transmission to the destination.
- Repeater: Networking device that regenerates or amplifies the incoming signal.
- Hub: It is a multi-port repeater.
- Bridge: Networking device that connects similar networks.
- Gateway: Network device that connects dissimilar networks.
- MODEM: Modulator Demodulator transfers analog signal into digital (Modulation) and vice versa (Demodulation)
- Multiplexer: It combines multiple incoming signals into one signal and the opposite is called a de-multiplexer.
Internet and its services
Define Internet. Explain services provided by the internet.
The Internet is a network that connects millions of users and devices all around the world together using TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol / Internet Protocol) and allows to share of data and information in between.
Services provided by the internet
- Email: The way of exchanging emails i.e messages between sender and receiver over the internet using a unique address (email address) is called email. Advantages of email: Faster, Cheaper, Reliable, Always available, Secured
- E-commerce: The process of buying and selling goods and services is called e-commerce. Eg, merogifts, amazon, Alibaba
- Telnet: It allows users to log in remotely to another user’s computer.
- IRC: Internet relay chat allows users to communicate in real-time.
- Video conferencing: It allows users to communicate in real time using video and audio signals.
Define web browser. Give some example
The application program which allows the user to browse web site from the internet is called a web browser. It establishes the communication between the user and the web server so that the user can access the content of the web. It uses HTTP (Hyper Text Transfer Protocol) to communicate. Eg, Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, Opera, Safari, Microsoft Edge (Internet Explorer), and Netscape navigator.
Differentiate between E-mail and postal service.
| Postal service | |
| It is the modern digital way of exchanging information. | It is the traditional way of exchanging information. |
| Use of computers and the internet. | Use of papers, post box, and post office. |
| It is faster and more reliable. | It is slower and nonreliable. |
| Recipient not required. | Recipient required. |
| It is always available 365 days a year. | It may not be always available |
| Highly secured. | Less secured. |
Differentiate between intranet and extranet.
| Intranet | Extranet |
| Private network accessible within the organization. | Private network accessible outside of the organization. |
| They are limited within the organization. | They are extended among its branch. |
Some important terminologies:
- ISP: Internet Service Provider
- SMTP: Simple Mail Transfer Protocol
- POP: Post Office Protocol
- URL: Uniform Resource Locator
- DARPA: Defense Advance Research Project Agency
- FTP: File Transfer Protocol
- ADSL: Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line
- CDMA: Code Division Multiple Access
- Web server: The storage location where every content of the website is stored.
- Home page: The introductory page or landing page of a website.
- Search engine: The web application which allows users to search content in WWW by using keywords. Eg, google, bing.
- Downloading: Transferring data and files from a web server to the user.
- Uploading: Transferring data and files from the user to the web server.